-
 Hsf1p-target genes (green) coalesce into foci after heat shock (nuclear pore complex, red).
Hsf1p-target genes (green) coalesce into foci after heat shock (nuclear pore complex, red).
Image courtesy of S. Chowdhary and A. Kainth, Gross Lab, LSU Health Sciences Center. -
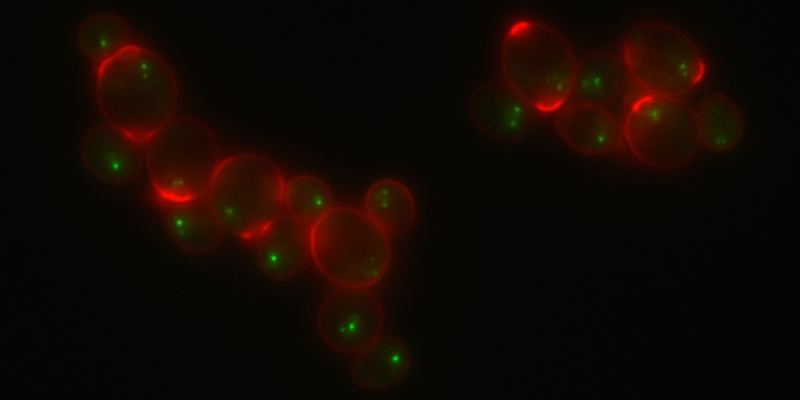 Rap1-GFP and Calcofluor White staining of stationary phase cells.
Rap1-GFP and Calcofluor White staining of stationary phase cells.
Image courtesy of M. Guidi, M. Ruault and A. Taddei, Institut Curie (Paris). -
 Pma1-mCherry and Vma1-GFP localization in mitotic cells.
Pma1-mCherry and Vma1-GFP localization in mitotic cells.
Image courtesy of M. Eastwood, Fred Hutch and M. Meneghini, University of Toronto. -
 CCCP-induced decrease of mitochondrial membrane potential (below) or control treatment (above) as measured by MitoLoc.
CCCP-induced decrease of mitochondrial membrane potential (below) or control treatment (above) as measured by MitoLoc.
Image courtesy of Dr. Jakob Vowinckel, Ralser Lab, University of Cambridge. -
 Redistribution of Msn5 pools from the nucleus to the cytoplasm upon glucose deprivation.
Redistribution of Msn5 pools from the nucleus to the cytoplasm upon glucose deprivation.
Image courtesy of H. Huang and A. Hopper, Ohio State University. -
 Floccule of yeast rho0 cells expressing PTS1-GFP as a peroxisomal marker, stained with calcofluor white.
Floccule of yeast rho0 cells expressing PTS1-GFP as a peroxisomal marker, stained with calcofluor white.
Image courtesy of Dr. Jakob Vowinckel, University of Cambridge -
 S. cerevisiae membrane proteins visualized by RFP and GFP.
S. cerevisiae membrane proteins visualized by RFP and GFP.
Image courtesy of Masur. Wikimedia Commons. -
 Peroxisome (red) and mitochondrial (green) fission defects in vps1 fis1 double deletion strain transformed with FIS1.
Peroxisome (red) and mitochondrial (green) fission defects in vps1 fis1 double deletion strain transformed with FIS1.
Image courtesy of S. Lefevre, S. Kumar and I. van der Klei, University of Groningen. -
 Yeast cells expressing TRK1/GFP.
Yeast cells expressing TRK1/GFP.
Image courtesy of V. Zayats and J. Ludwig, Center of Nanobiology and Structural Biology, AV CR. -
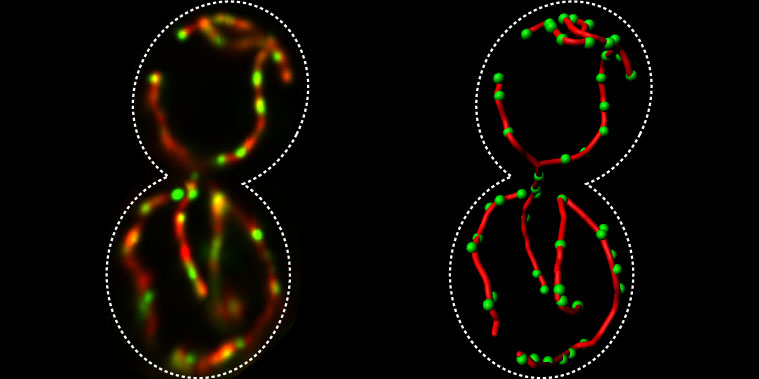 The distribution of mtDNA (green) within the mitochondrial network (red).
The distribution of mtDNA (green) within the mitochondrial network (red).
Image courtesy of Christof Osman and Peter Walter, University of California, San Francisco -
 The distribution of ER exit sites (ERES, green) within the ER (red).
The distribution of ER exit sites (ERES, green) within the ER (red).
Image courtesy of A. Nakano and K. Kurokawa, RIKEN. -
 Cell, actin and nuclear morphology of yeast cells treated with DMSO (left) and poacic acid (right).
Cell, actin and nuclear morphology of yeast cells treated with DMSO (left) and poacic acid (right).
Images courtesy of Hiroki Okada and Yoshikazu Ohya, University of Tokyo. -
 Localization of active Ras in a wild type strain
Localization of active Ras in a wild type strain
Image courtesy of S. Colombo and E. Martegani, University Milano Bicocca -
 Sectored colonies showing loss of silencing at the HML locus
Sectored colonies showing loss of silencing at the HML locus
Image courtesy of Anne Dodson, UC Berkeley -
 Pma1p imaged using the RITE tagging system in mother (green) and daughter cells (red)
Pma1p imaged using the RITE tagging system in mother (green) and daughter cells (red)
Image courtesy of Dan Gottschling Ph.D., Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center -
 Lipid droplets in fld1 mutant images by CARS
Lipid droplets in fld1 mutant images by CARS
Image courtesy of Heimo Wolinski, Ph.D. and Sepp D. Kohlwein, Ph.D., University of Graz, Austria -
 Fpr3p accumulation in the nucleolus of S. cerevisiae
Fpr3p accumulation in the nucleolus of S. cerevisiae
Image courtesy of Amy MacQueen, Ph.D., Wesleyan University
anti-Fpr3 antibody courtesy of Jeremy Thorner, Ph.D., UC Berkeley -
 San1 strain visualized with FUN and calcofluor white
San1 strain visualized with FUN and calcofluor white
Image courtesy of the Bruschi lab, ICGEB, Trieste, Italy -
 Single MDN1 mRNAs detected by FISH
Single MDN1 mRNAs detected by FISH
Image courtesy of the Zenklusen Lab, Université de Montréal -
 Localization of Ace2-GFP to daughter cell nuclei
Localization of Ace2-GFP to daughter cell nuclei
Image courtesy of Eric Weiss, Ph.D. Northwestern University
About SGD
The Saccharomyces Genome Database (SGD) provides comprehensive integrated biological information for the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae along with search and analysis tools to explore these data, enabling the discovery of functional relationships between sequence and gene products in fungi and higher organisms.
Give a Gift/Support SGD
Your generous gift to SGD enables us to continue providing essential information for your research and teaching efforts. Donations are now critical for our work to continue and are greatly appreciated.
To contribute using a credit card, please use this form: give.stanford.edu.
- Under ‘Direct your gift,’ select ‘Other Stanford Designation’ from the pulldown menu
- In the ‘Other’ text box, specify SGD by including the text “Saccharomyces Genome Database - Account : GHJKO, Genetics : WAZC”
- Complete the form and payment to donate to SGD
If you’d like to contribute by check, please contact us at: sgd-helpdesk@lists.stanford.edu
Thank you for your support!
Meetings
July 21 to July 24, 2025 -
Sorbonne University, Paris, France
July 22 to August 12, 2025 -
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
August 03 to August 08, 2025 -
Boston College, Boston, MA
August 06 to August 08, 2025 -
Web-based platform
September 01 to September 05, 2025 -
Warsaw University, Warsaw, Poland
March 17 to March 22, 2026 -
Asilomar Conference Grounds, Pacific Grove, CA
New & Noteworthy
About this newsletter:This is the Spring 2025 issue of the SGD newsletter. The goal of this newsletter is to inform our users about new features in SGD and to foster communication within the yeast community. Contents Give a Gift / Support SGD: Credit Cards Now Accepted Budget cuts from NIH continue to strain SGD’s finances. […]
Read MoreYeastPathways, the database of metabolic pathways and enzymes in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is manually curated and maintained by the biocuration team at SGD. This resource is jam-packed with information, but somewhat hidden from view. We have been doing different things recently to make the pathways more readily accessible. Some time ago we added a […]
Read MoreFor over 50 years, the legendary Yeast Genetics & Genomics course has been taught each summer at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, though the name didn’t include “Genomics” in the beginning. The list of people who have taken the course reads like a Who’s Who of yeast research, including Nobel laureates and many of today’s leading […]
Read MoreGiving to SGD just got easier! We now accept donations by credit card with this form: give.stanford.edu. Select ‘Other Stanford Designation’ under ‘Direct your gift’ & in the ‘Other’ box, add: Saccharomyces Genome Database – Account: GHJKO, Genetics: WAZC. Thanks for your support! Your generous gift to SGD enables us to continue providing essential information […]
Read MoreAbout this newsletter:This is the December 2024 issue of the SGD newsletter. The goal of this newsletter is to inform SGD users about new features from SGD and to foster communication within the yeast community. Contents AlphaFold protein structures now on SGD protein pages We are thrilled to announce that we have now integrated AlphaFold protein structures […]
Read More